VP – Cell Segmentation & Tracking Showcase
Project Overview
This project implements a complete segmentation pipeline on the Cell Tracking Challenge dataset using both classical machine-learning models and a deep-learning U-Net.
Dataset
- Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 (2D fluorescent microscopy)
- Training & evaluation using Track 01 ST (silver-truth) masks
Goals
- Implement the full classical baseline (Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, SVMs, MLP)
- Add a graduate-level deep learning segmentation model (U-Net)
- Evaluate using Mean IoU (Jaccard) via
MySEGMeasure.pywrapper - Produce a clear, fully reproducible research pipeline and results page
Workflow Summary
1. Data Preparation
- Downloaded the Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 dataset using:
python scripts/setup_data.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --splits training test- Data is stored under:
artifacts/datasets/Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1/
training/
01, 01_ST, 01_GT, ...
02, 02_ST, 02_GT, ...
test/- ST masks are used for training and evaluation.
2. Classical Segmentation Pipeline
- Extract per-pixel features from a 5×5 sliding window around each pixel.
- Construct a balanced training set (foreground/background sampling).
-
Train the following classical models on these handcrafted features:
- Naive Bayes
- Logistic Regression
- Linear SVM
- RBF SVM
- MLP (1–hidden-layer neural network)
3. Deep Model (U-Net)
- Implemented a small U-Net in PyTorch.
- Trained the U-Net directly on raw image patches + ST masks.
- Evaluated predictions using the same IoU / SEGMeasure evaluation tools, for a fair comparison with classical models.
Segmentation Results (Track 01, ST Masks)
All results below are reported on Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1, Track 01, ST masks, using Mean IoU / Jaccard.
| Model | Mean IoU |
|---|---|
| Naive Bayes | 0.763 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.829 |
| SVM (RBF Kernel) | 0.817 |
| SVM (Linear) | 0.831 |
| MLP (Shallow NN) | 0.866 |
| U-Net (Deep Model) | 0.811 |
IoU Bar Chart
A visual comparison of Mean IoU across all models:
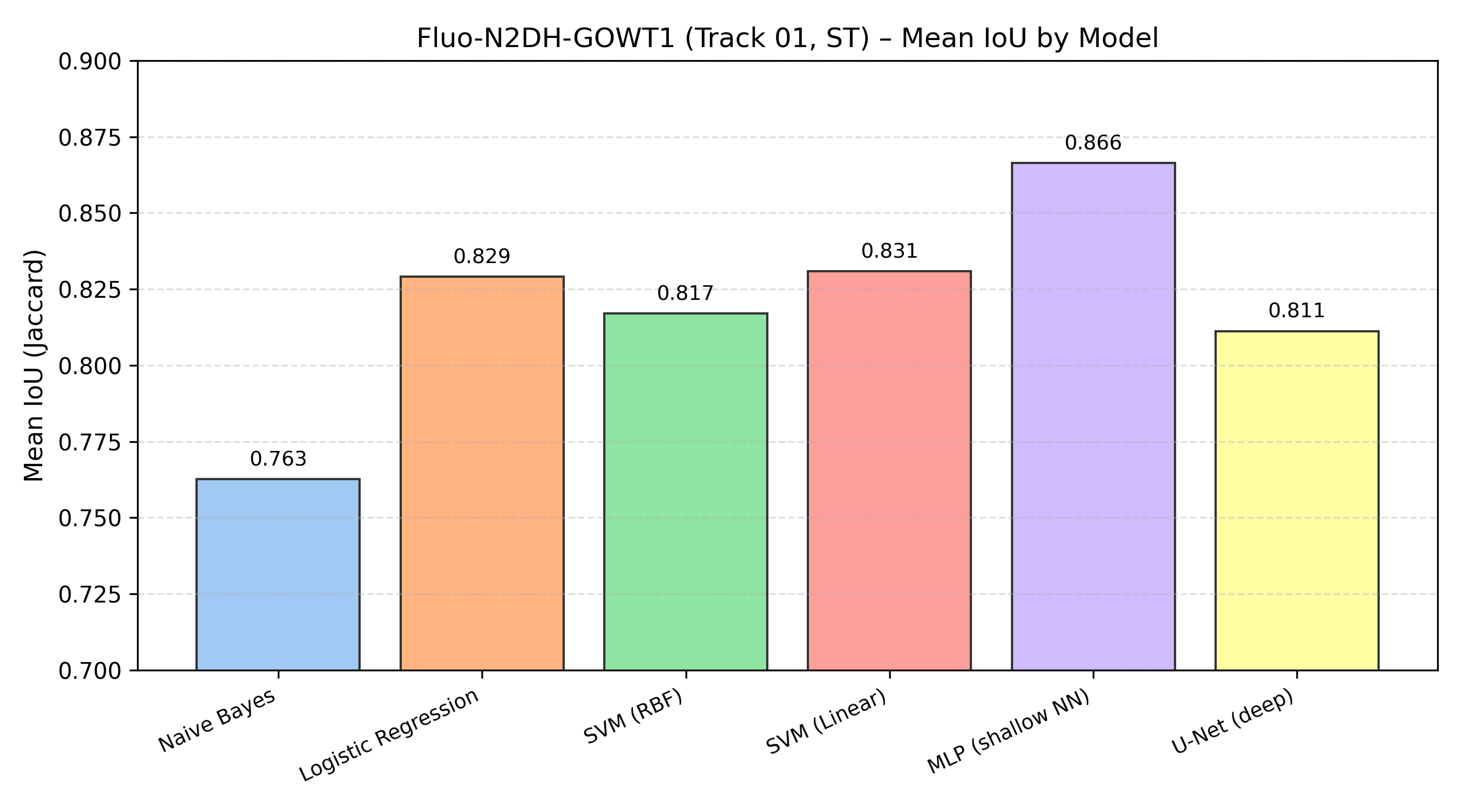
This bar chart summarizes the segmentation performance of all classical baselines and the deep U-Net on the same track and silver-truth masks.
Qualitative Results (Example Frame t000)
Below is a qualitative comparison for time frame t000.
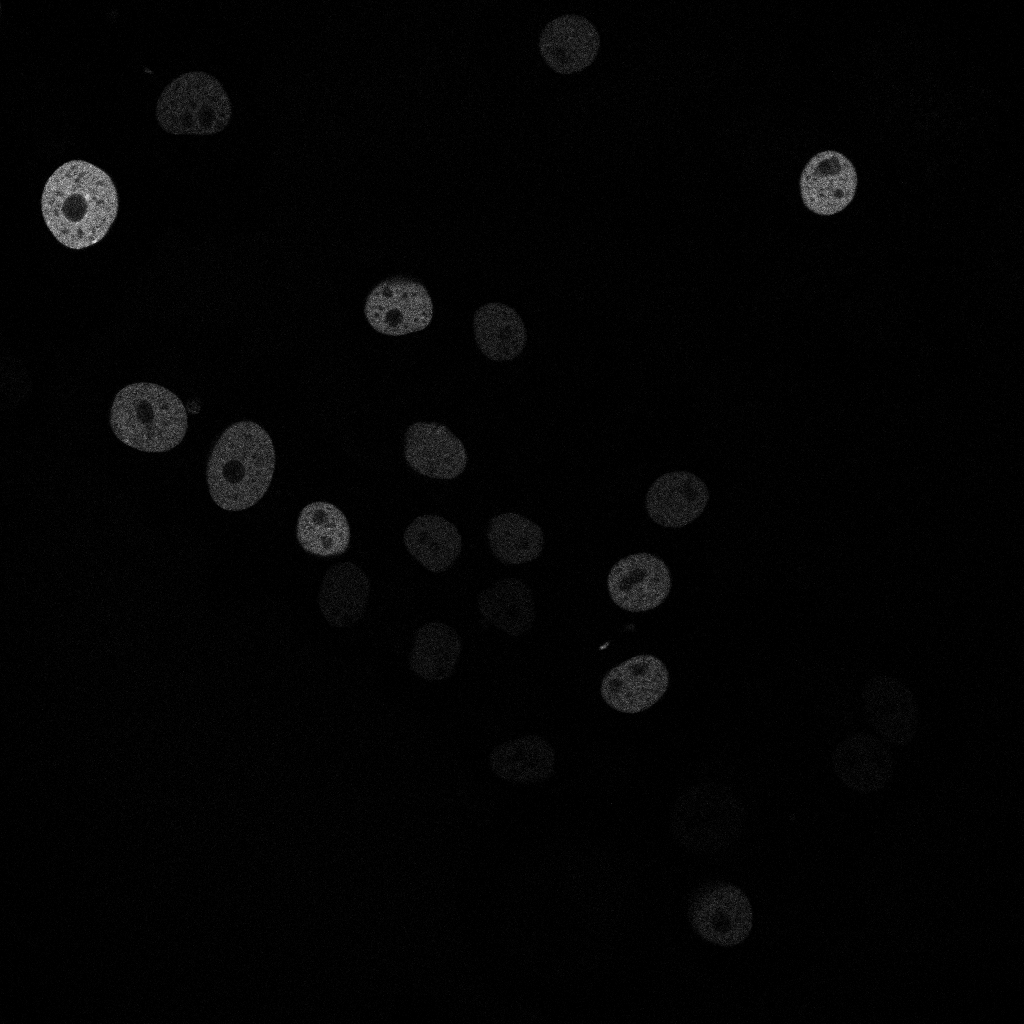
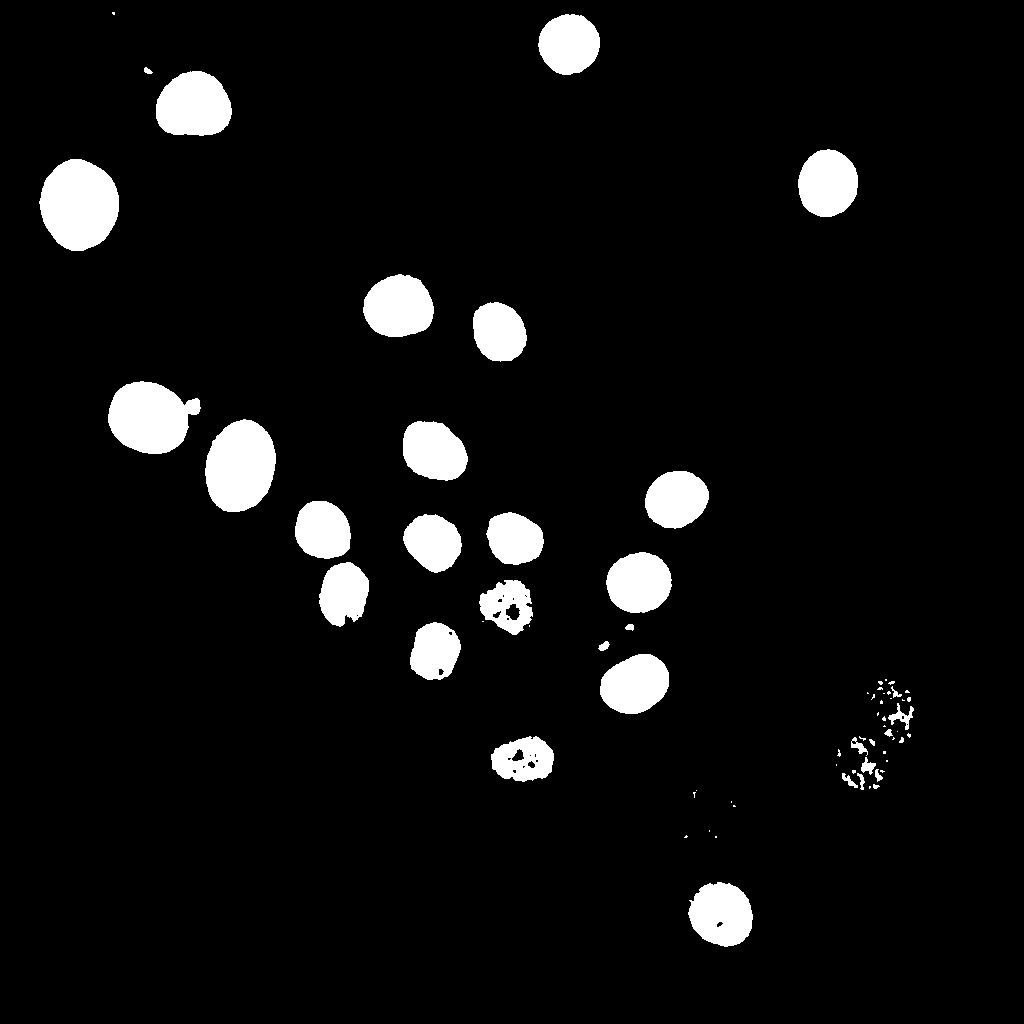

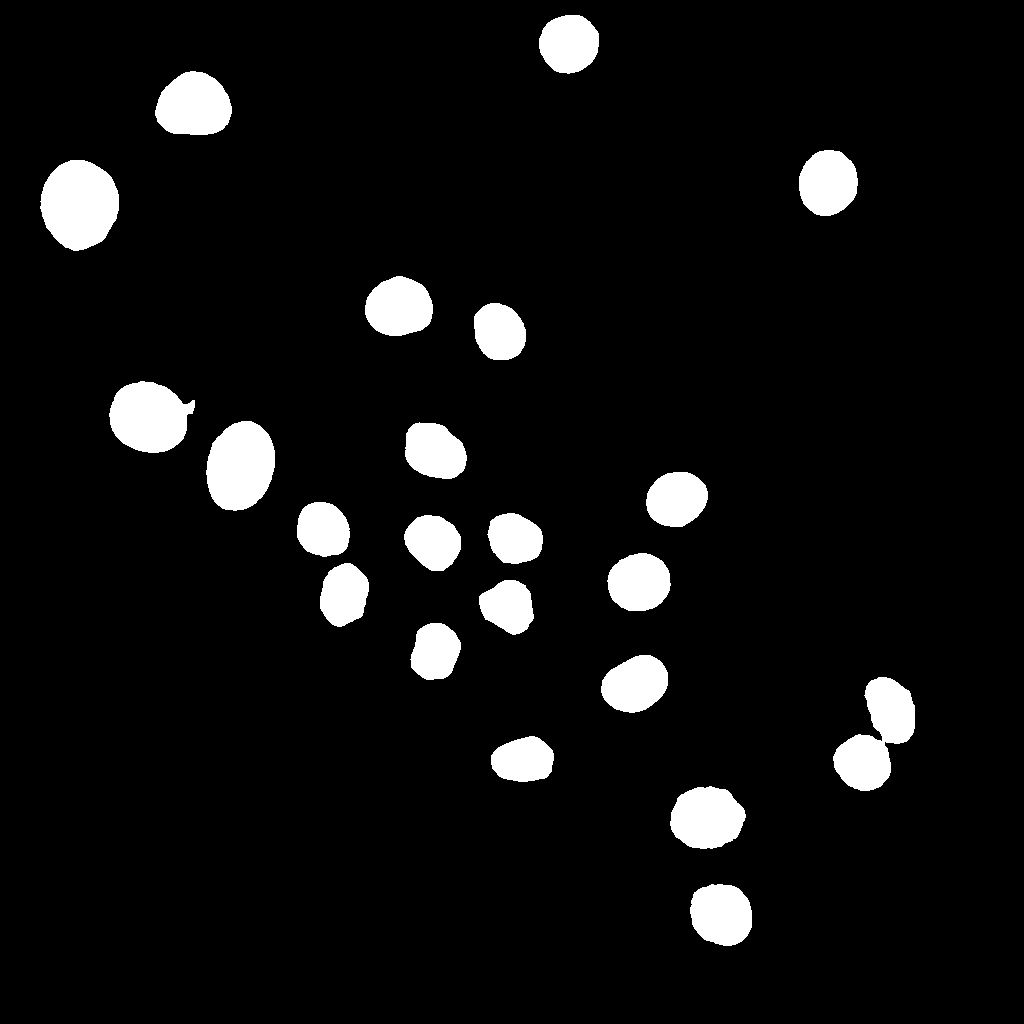

Classical Pipeline Details
Feature Extraction
- For each pixel, a 5×5 neighborhood is extracted from the raw image.
- The 5×5 patch is flattened into a 25-dimensional feature vector.
- Optional normalization / scaling can be applied.
-
Training data is formed by sampling pixels from:
- Foreground regions (cells) in ST masks
- Background regions
Classical Models Overview
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Naive Bayes | Very fast generative baseline; strong bias, high variance on noisy patches |
| Logistic Regression | Linear discriminative model; good trade-off between speed and performance |
| Linear SVM | Margin-based linear classifier; robust on this feature space |
| RBF SVM | Non-linear classifier; higher capacity but limited gain here |
| MLP (Shallow NN) | One-hidden-layer neural network on handcrafted features; best classical IoU |
Each model produces a probability or score per pixel, which is converted into a binary segmentation mask and then evaluated via IoU and SEGMeasure.
Deep Model: U-Net
Architecture (Simplified)
Input (1 × H × W)
↓
Encoder: [Conv → ReLU → Downsample] × 4
↓
Bottleneck
↓
Decoder: [Upsample → Skip Connection → Conv → ReLU] × 4
↓
Output (1 × H × W logits)
↓
Sigmoid → Binary maskSkip connections from encoder to decoder help preserve fine-grained spatial detail, which is crucial for accurate cell boundaries.
Training Settings
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 10 |
| Batch Size | 4 |
| Loss | BCEWithLogitsLoss |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Hardware | CPU |
Even under these modest settings, the U-Net produces sharp and realistic masks, especially for medium-to-large cells.
Reproduction Checklist
This section describes how to reproduce the main experiments from a fresh clone of the repo.
1. Environment Setup
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate cse488-cell-tracking
pip install -e .2. Download Dataset
python scripts/setup_data.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --splits training test3. Train Classical Models (Example Commands)
# Naive Bayes
python scripts/train_naive_bayes.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01
# Logistic Regression
python scripts/train_logreg.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01
# SVM with RBF kernel
python scripts/train_svm.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --kernel rbf
# Linear SVM
python scripts/train_svm_linear.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01
# MLP (shallow neural net)
python scripts/train_mlp.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01
Each script saves the trained model into artifacts/models/
(e.g., nb_track01.pkl, logreg_track01.pkl,
etc.).
4. Train U-Net
python scripts/train_unet.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --epochs 10 --batch-size 4 --lr 0.001 --model-path artifacts/models/unet_track01.pt5. Evaluate Models
Example evaluation commands (with verbose per-label IoU):
# Naive Bayes
python scripts/eval_seg.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --model-type naive_bayes --model-path artifacts/models/nb_track01.pkl --verbose
# Logistic Regression
python scripts/eval_seg.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --model-type logreg --model-path artifacts/models/logreg_track01.pkl --verbose
# Linear SVM
python scripts/eval_seg.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --model-type svm --model-path artifacts/models/svm_linear_track01.pkl --verbose
# MLP
python scripts/eval_seg.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --model-type mlp --model-path artifacts/models/mlp_track01.pkl --verbose
# U-Net
python scripts/eval_seg.py Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 --track 01 --model-type unet --model-path artifacts/models/unet_track01.pt --verbose
The script reports Mean IoU (Jaccard) and per-label IoU values, along
with a summary Jaccard index consistent with
MySEGMeasure.py.
Conclusion
This project successfully reproduces the required classical segmentation baseline and extends it with a U-Net deep-learning model on the Fluo-N2DH-GOWT1 dataset.
- The MLP achieved the highest Mean IoU (≈0.866) among all classical models.
- The U-Net achieved ≈0.811 Mean IoU, performing extremely well on large cells but missing some very small objects due to limited training and lack of augmentation.
Overall, the repository provides a fully reproducible, modular, and extensible segmentation system, ready for future improvements such as:
- Stronger data augmentation
- Dice / Focal / Tversky losses
- Multi-track training
- Temporal tracking and linking of cell identities over time
Project Links
-
GitHub Repository:
https://github.com/panchav07/CSE488-VP_Project-Cell-Tracking -
Cloudflare Pages Site:
https://cse488-vp-project-cell-tracking.pages.dev/

